Exploring the Health Consequences: The Impact of a Sedentary Lifestyle
Understanding the Sedentary Dilemma: A Modern Health Epidemic
In an increasingly sedentary world, the lack of exercise has emerged as a significant health concern. Uncover the multifaceted impact of a sedentary lifestyle on overall well-being and delve into the imperative need for regular physical activity.
Cardiovascular Complications: The Silent Threat of Inactivity
The heart thrives on movement, and a sedentary lifestyle poses a silent threat to cardiovascular health. Lack of exercise contributes to elevated blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and an increased risk of heart disease. Understanding the link between inactivity and cardiovascular complications emphasizes the importance of incorporating regular physical activity into daily life.
Weight Management Woes: Sedentary Habits and Obesity
The lack of physical activity is a prominent contributor to the global obesity epidemic. Sedentary habits, coupled with poor dietary choices, lead to weight gain and obesity. Excess weight not only affects physical appearance but also increases the risk of various health conditions, including diabetes, joint problems, and certain cancers.
Muscle Atrophy and Skeletal Health: The Consequences of Inactivity
The human body is designed for movement, and when deprived of regular exercise, muscles atrophy and weaken. Sedentary individuals often experience decreased muscle mass, compromising strength and agility. Furthermore, the lack of weight-bearing activity negatively impacts bone density, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
Metabolic Disruptions and Insulin Resistance: Inactivity’s Toll on Metabolism
Regular physical activity is essential for a well-functioning metabolism. Inactivity, on the other hand, contributes to metabolic disruptions and insulin resistance. This creates a predisposition to conditions such as type 2 diabetes, where the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar is compromised. Combatting inactivity is a crucial aspect of diabetes prevention and management.
Mental Health Struggles: The Mind-Body Connection
The mind and body are intricately connected, and the lack of exercise can take a toll on mental health. Physical activity is known to release endorphins, the body’s natural mood elevators. Sedentary behavior, conversely, is linked to an increased risk of anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline. Recognizing the mind-body connection underscores the importance of movement for holistic well-being.
Reduced Immune Vigilance: The Impact on Disease Resistance
Regular exercise supports a robust immune system, enhancing the body’s ability to fend off infections and diseases. Inactivity, conversely, compromises immune function. Sedentary individuals may find themselves more susceptible to illnesses, highlighting the role of physical activity in maintaining optimal immune vigilance.
Sleep Disruptions and Fatigue: The Sedentary Sleep Cycle
The relationship between physical activity and quality sleep is well-established. Lack of exercise can contribute to sleep disruptions and increased fatigue. The sedentary sleep cycle often involves difficulty falling asleep and experiencing restless nights. Prioritizing regular exercise can promote better sleep patterns and overall sleep quality.
Social Isolation and Lifestyle Impact: The Sedentary Society
Sedentary habits can contribute to social isolation and impact overall lifestyle. Individuals who lead inactive lives may miss out on opportunities for social engagement and community participation. Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle is often associated with prolonged periods of screen time, contributing to a more isolated and less socially connected society.
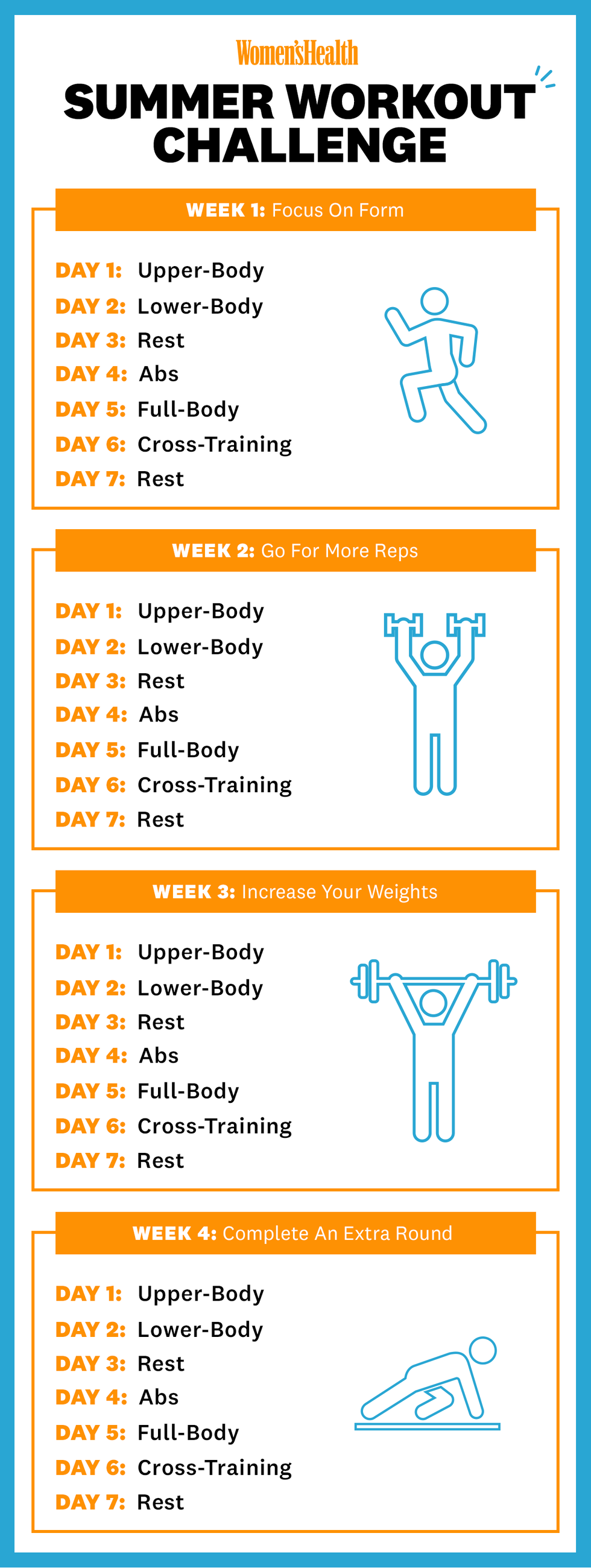
Breaking the Sedentary Cycle: Strategies for a Healthier Lifestyle
Breaking free from a sedentary lifestyle involves intentional efforts to incorporate more movement into daily routines. From desk exercises to regular walks and structured workouts, finding enjoyable ways to stay active is key. Adopting small, sustainable changes gradually builds a foundation for a healthier, more active lifestyle.
Lack of Exercise Health: Choose Movement, Choose Well-being
For additional insights and resources on the impact of a sedentary lifestyle on health and strategies for embracing an active life, explore Lack of Exercise Health. Choose movement for a healthier, more vibrant life.